The DMA defines in Article 2 the "groundwater body" as "a clearly differentiated volume of groundwater in an aquifer or aquifer".
A total of 63 groundwater bodies defined in the Segura demarcation in the 2015/21 planning cycle are included in the Segura hydrographic basin.
| Code | Name | Associated surface mass |
|---|---|---|
| 70.001 | Corral Rubio | ES0703190001 |
| 70.002 | Sinclinal de la Higuera | - |
| 70.003 | Alcadozo | ES0701010304 |
| 70.004 | Boquerón | - |
| 70.005 | Tobarra-Tedera-Pinilla | - |
| 70.006 | Pino | ES0701010306 |
| 70.007 | Conejeros-Albatana | - |
| 70.008 | Ontur | - |
| 70.009 | Sierra de la Oliva | - |
| 70.010 | Pliegues Jurásicos del Mundo | ES0701010109 |
| ES0701010304 | ||
| 70.011 | Cuchillos-Cabras | - |
| 70.012 | Cingla | - |
| 70.013 | Moratilla | - |
| 70.014 | Calar del Mundo | ES0701010304 |
| 70.015 | Segura-Madera-Tus | ES0701010103 |
| ES0701010104 | ||
| 70.016 | Fuente Segura-Fuensanta | ES0701010103 |
| ES0701010104 | ||
| ES0701010106 | ||
| ES0701010107 | ||
| ES0701011101 | ||
| ES0701011103 | ||
| ES0701011104 | ||
| 70.017 | Acuíferos inferiores de la Sierra del Segura | - |
| 70.018 | Machada | ES0701010106 |
| 70.019 | Taibilla | - |
| 70.020 | Anticlinal de Socovos | ES0701010109 |
| ES0701011803 | ||
| ES0701011804 | ||
| 70.021 | El Molar | ES0701010306 |
| 70.022 | Sinclinal de Calasparra | ES0701010113 |
| ES0701010114 | ||
| 70.023 | Jumilla-Yecla | - |
| 70.024 | Lácera | - |
| 70.025 | Ascoy-Sopalmo | - |
| 70.026 | El Cantal-Viña Pi | - |
| 70.027 | Serral-Salinas | - |
| 70.028 | Baños de Fortuna | ES0701010113 |
| ES0701010114 | ||
| 70.029 | Quíbas | ES0701012601 |
| ES0701012602 | ||
| 70.030 | Sierra del Argallet | - |
| 70.031 | Sierra de Crevillente | - |
| 70.032 | Caravaca | ES0701011803 |
| ES0701011804 | ||
| ES0701011901 | ||
| ES0701011903 | ||
| ES0701012002 | ||
| ES0701012004 | ||
| 70.033 | Bajo Quípar | ES0701012002 |
| ES0701012004 | ||
| 70.034 | Oro-Ricote | ES0701010113 |
| ES0701010114 | ||
| 70.035 | Cuaternario de Fortuna | - |
| 70.036 | Vega Media y Baja del Segura | ES0702100001 |
| ES0702080115 | ||
| ES0702080116 | ||
| 70.037 | Sierra de la Zarza | ES0701012002 |
| ES0701012004 | ||
| 70.038 | Alto Quípar | ES0701012002 |
| ES0701012004 | ||
| ES0701010203 | ||
| 70.039 | Bullas | ES0701012303 |
| ES0701012301 | ||
| 70.040 | Sierra Espuña | ES0701012306 |
| ES0701012307 | ||
| 70.041 | Vega Alta del Segura | ES0702080115 |
| ES0702080116 | ||
| 70.042 | Terciario de Torrevieja | - |
| 70.043 | Valdeinfierno | ES0701010203 |
| 70.044 | Vélez Blanco-María | - |
| 70.045 | Detrítico de Chirivel-Maláguide | ES0701012901 |
| ES0701012902 | ||
| 70.046 | Puentes | ES0701010205 |
| 70.047 | Triásico Maláguide de Sierra Espuña | - |
| 70.048 | Santa-Yéchar | - |
| 70.049 | Aledo | - |
| 70.050 | Bajo Guadalentín | - |
| 70.051 | Cresta del Gallo | - |
| 70.052 | Campo de Cartagena | - |
| 70.053 | Cabo Roig | - |
| 70.054 | Triásico de las Victorias | - |
| 70.055 | Triásico de Carrascoy | - |
| 70.056 | Sierra de las Estancias | - |
| 70.057 | Alto Guadalentín | - |
| 70.058 | Mazarrón | - |
| 70.059 | Enmedio-Cabezo de Jara | - |
| 70.060 | Las Norias | - |
| 70.061 | Águilas | - |
| 70.062 | Sierra de Almagro | - |
| 70.063 | Sierra de Cartagena | - |
The location and boundaries of defined groundwater bodies are shown in the following figure:
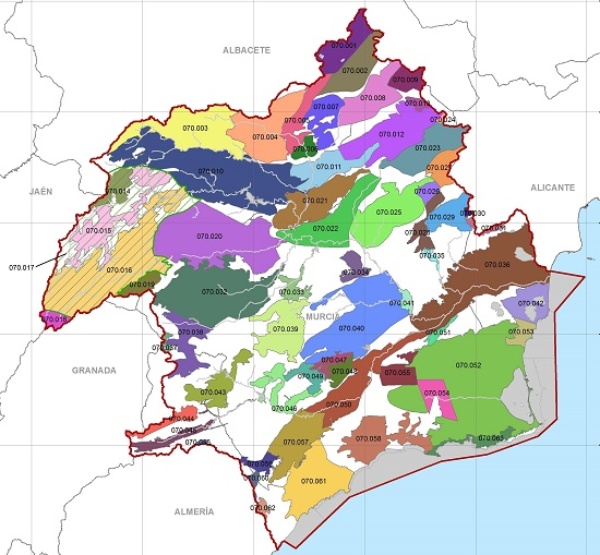
Underground water bodies in the DHS
It is available in Annex 12. Characterization of the water bodies of the Segura Hydrographic Demarcation ![]() (18.1 MB), of the Segura Basin Hydrological Plan, more detailed information on the characterization of groundwater bodies and on the poster (A0) of groundwater bodies
(18.1 MB), of the Segura Basin Hydrological Plan, more detailed information on the characterization of groundwater bodies and on the poster (A0) of groundwater bodies ![]() (7.4 MB).
(7.4 MB).
With respect to the quality of the groundwater of the demarcation, the Segura Hydrographic Confederation has a network to monitor the state of these bodies of water, where a sample is taken and analyzed. For more information, you can consult the following links:
As for the control of the piezometric level, the Segura Hydrographic Confederation has a network that is currently integrated by more than 130 control points, distributed among the different bodies of groundwater in the basin. The measurement of the piezometric level in each mass, is made from the verification of the depth to which the water is found, in some of the existing probes.
To obtain information about this network, you can consult
Among the bodies of water that have a greater number of control points are those in which most of the extractions of groundwater in the Segura basin are located, such as the Campo de Cartagena, Caravaca, Vegas Baja And Middle of the Segura, Socovos Anticlinal, Alto Guadalentín, Bajo Guadalentín, Ascoy-Sopalmo, Boquerón, Bullas, El Molar, Mazarrón, Jurassic Folds of the World, Knives-Goats, Sierra Espuña, Cingla, Eagles and Sinclinal of Calasparra.